Note-taking is one of the most important learning skills, yet many beginners struggle to do it effectively. Some write too much, others write too little, and many simply copy information without understanding it. Good note-taking is not about writing everything—it is about capturing key ideas in a clear, organized, and useful way.
For beginners, learning effective note-taking methods can improve understanding, memory, and overall study performance. With the right techniques, notes become a powerful tool for learning rather than a boring task.
Why Note-Taking Matters
Note-taking helps the brain process information actively. When you listen, read, and write at the same time, your mind stays engaged. Notes also serve as a personal reference that makes revision faster and easier.
 Well-structured notes save time, reduce confusion, and improve exam preparation. For beginners, developing good note-taking habits early builds a strong foundation for lifelong learning.
Well-structured notes save time, reduce confusion, and improve exam preparation. For beginners, developing good note-taking habits early builds a strong foundation for lifelong learning.
Common Note-Taking Mistakes Beginners Make
Before learning effective methods, it is important to understand common mistakes:
-
Writing everything word for word
-
Not organizing notes properly
-
Using unclear handwriting or random formats
-
Never reviewing or revising notes
Avoiding these mistakes makes note-taking more meaningful and effective.
Start With the Right Mindset
Good notes are not a transcript of a lecture or textbook. They are a summary written in your own words. Beginners should focus on understanding the topic first and then writing key points.
Always aim for clarity over quantity. Simple, clear notes are more useful than long, confusing pages.
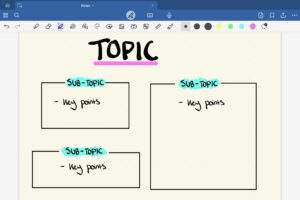
The Outline Method
The outline method is one of the easiest note-taking techniques for beginners. It organizes information in a structured, hierarchical format using headings and bullet points.
Main topics are written as headings, while subtopics and details are indented underneath. This method works well for lectures, textbooks, and theory-based subjects.
The outline method helps beginners see the relationship between ideas and makes revision quicker.
The Cornell Note-Taking Method
The Cornell method is a highly effective system that improves understanding and revision. In this method, a page is divided into three sections:
-
A narrow left column for keywords or questions
-
A larger right section for detailed notes
-
A summary section at the bottom
During or after studying, students write questions or keywords in the left column and summarize the topic at the bottom. This method encourages active recall and better retention.
For beginners, the Cornell method is excellent for building strong study habits.
The Mind Mapping Method
Mind mapping is a visual note-taking technique that helps beginners understand complex topics. Instead of writing linear notes, ideas are connected around a central concept using branches.
This method works especially well for brainstorming, revision, and subjects that involve relationships between ideas. Mind maps improve creativity and help learners see the bigger picture.
Beginners who prefer visual learning often find mind maps easier and more engaging.
The Sentence Method
The sentence method involves writing information in short, clear sentences, each on a new line. This method is useful when information is fast-paced, such as in lectures.
Although this method may lack structure initially, beginners can later organize and revise the notes. It is a good starting point for those who are still developing note-taking confidence.
Use Abbreviations and Symbols
Writing every word slows down note-taking. Beginners should learn to use abbreviations, symbols, and short forms. For example, using arrows for cause-and-effect, symbols for important points, or shortened words for common terms.
This makes note-taking faster and more efficient while maintaining clarity.
Focus on Keywords and Concepts
Instead of writing long paragraphs, focus on keywords, definitions, formulas, examples, and important ideas. Highlight or underline key terms to make them stand out.
Notes should help trigger memory, not replace textbooks.
Review and Revise Notes Regularly
One of the most important habits beginners often ignore is reviewing notes. Revising notes within 24 hours helps reinforce learning and clarify doubts.
Add missing points, rewrite unclear sections, and organize notes after class or study sessions. This process turns rough notes into valuable study material.
Digital vs Handwritten Notes
Both digital and handwritten notes have advantages. Handwritten notes improve memory and focus, while digital notes are easy to edit, store, and search.
Beginners should choose the method that suits their learning style. Some may prefer handwritten notes for understanding and digital notes for revision.
Develop a Consistent Note-Taking Style
Consistency improves efficiency. Using the same format, symbols, and structure makes notes easier to read and revise. Over time, beginners develop a personal note-taking style that suits their learning needs.
Conclusion
Effective note-taking is a skill that improves with practice. For beginners, the goal is not perfection but clarity and consistency. By using structured methods, focusing on key ideas, and regularly reviewing notes, learners can transform note-taking into a powerful learning tool.
Good notes reduce study time, improve understanding, and build confidence. With the right approach, note-taking becomes an essential habit that supports academic success and lifelong learning.